
“Look for the padlock icon in your browser bar when logging in. This tells you that the site you’re entering your details into is secure.“
– nectar.com
That’s the advice I recently received in a generic mass “Keeping you safe” email from Nectar, a loyalty points scheme here in the UK, which was sent to all their customers.
Whilst you should ensure that the websites you frequent have a “padlock” icon in your browser’s address bar, your browser will make it quite clear if the site you’re visiting isn’t secure.
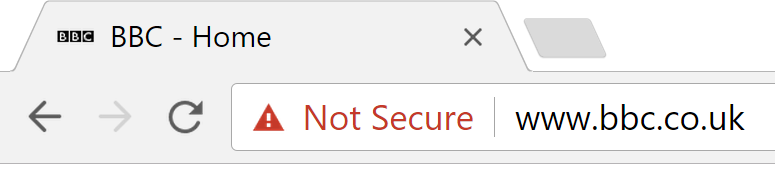
But you should never rely on a padlock icon itself as an indication of a website’s legitimacy or trustworthiness!
Life before the “s”
Now, when the internet was in its infancy, every website you would access had an address (or URL) which began “http://”.
As the internet grew and evolved, there was a greater need for stronger security and encryption between your browser and the website you were visiting. This was especially true for shopping and banking websites where sensitive data would be passing between browser and website.
The all important “s”
So along came “https” (the “s” standing for “Secure”). Under https, the connection between your browser and the website you’re visiting is encrypted.
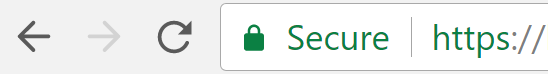
In order to facilitate access to a website via encrypted https, the website owner would need to install a security certificate on their website.
In the early days of https, security certificates were not always cheap for webmasters to obtain, and could often costing hundreds of dollars a piece.
But that was then.. today, security certificates are free from many services, such as the excellent LetsEncrypt.
So whereas once upon a time scammers setting up fake websites wouldn’t necessarily bother with expensive security certificates to make their fake websites secure, nowadays it’s free, quick and easy to install a security certificate to a website.
Therefore, yes, the presence of a padlock icon in your browser’s address bar is an indication that the connection between your browser and the website is securely encrypted. However, it is not a validation of the legitimacy or trustworthiness of the website you’re connecting to.
Let’s face it, most websites these days have security certificates installed, and your browser will make it very obvious if they don’t.
So rather than looking for a padlock icon, take the time instead to read the actual URL shown in your browser’s address bar, to make sure you’re viewing the website you intend to!
Quite often scammers will set up fake websites to look like their genuine counterparts, and perhaps just change a single character in the domain name, so that at quick glance it looks very similar to a real site.
For instance “reddit.com” and “reddlt.com” look very similar to the casual eye, but only one is the real Reddit website.
